Standards and Methodologies
We are committed to deliver professional services at highest standards, therefore we have invested in best standards, methodologies and frameworks. Our experienced engineers have been developed working methodologies aligned with best security and testing practices.
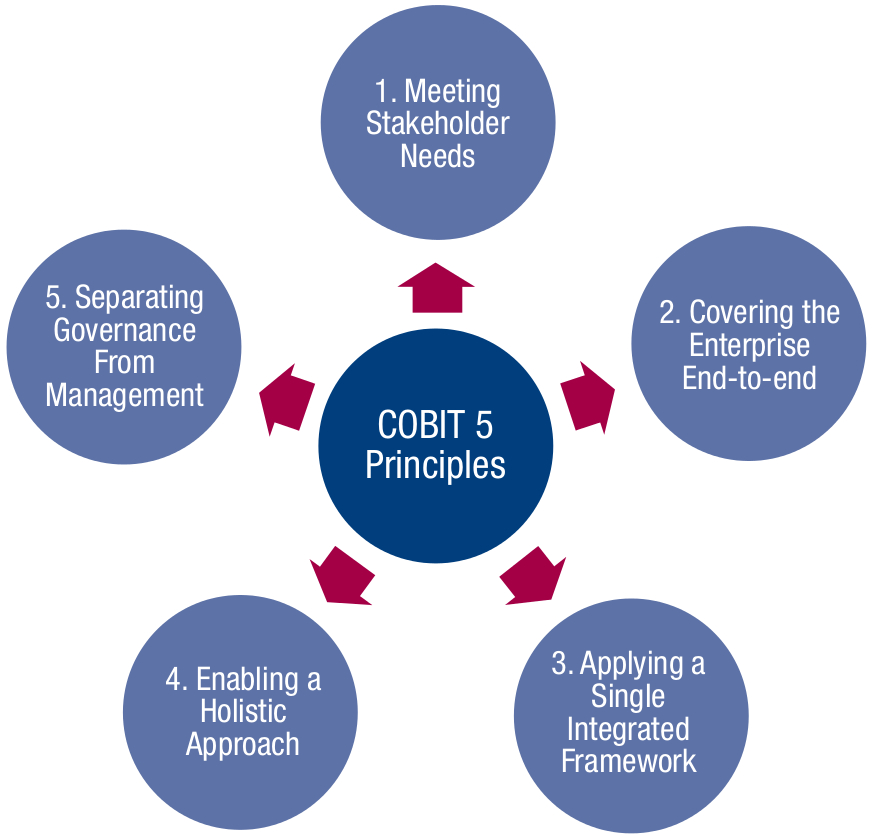
- COBIT 5 - COBIT 5 provides a comprehensive framework that assists enterprises in achieving their objectives for the governance and management of enterprise IT. It helps enterprises to create optimal value from IT by maintaining a balance between realising benefits and optimising risk levels and resource use. COBIT 5 enables IT to be governed and managed in a holistic manner for the entire enterprise, taking in the full end-to-end business and IT functional areas of responsibility, considering the IT-related interests of internal and external stakeholders. COBIT 5 is generic and useful for enterprises of all sizes, whether commercial, not-for-profit or in the public sector. Processes for Governance of Enterprise IT designed to Evaluate, Direct and Monitor: EDM01 Ensure Governance Framework Setting and Maintenance; EDM02 Ensure Benefits Delivery; EDM03 Ensure Risk Optimisation; EDM04 Ensure Resource Optimisation; EDM05 Ensure Stakeholder Transparency. Processes for Management of Enterprise IT are grouped in four categories: Align, Plan and Organise, Build, Acquire and Implement, Deliver, Service and Support, Monitor, Evaluate and Assess.
- ISO 27000 Series - The ISO 27000 series provides best practice recommendations on information security management, risks and controls within the context of an overall information security management system (ISMS). The most widely used are: ISO/IEC 27000 - Information security management systems - Overview and vocabulary. ISO/IEC 27001 - Information technology - Security Techniques - Information security management systems and ISO/IEC 27002 - Code of practice for information security management. ISO/IEC 27003 — Information security management system implementation guidance. ISO/IEC 27004 - Information security management – Measurement. ISO/IEC 27005 - Information security risk management. ISO/IEC 27006 - Requirements for bodies providing audit and certification of information security management systems. ISO/IEC 27007 - Guidelines for information security management systems auditing (focused on the management system). ISO/IEC TR 27008 - Guidance for auditors on ISMS controls (focused on the information security controls).
- ISO 14298 - Graphic technology - Management of security printing processes. This International Standard specifies requirements for a security printing management system for security printers, prescribing which elements a security printing management system contains and how a specific organization implements these elements. When implemented, the security printing management system: a) achieves the security of products, processes, means of production, premises, information, raw material supplies; b) is used to continue to meet demonstrably the requirements, and naturally, the needs of customers; c) affords management the confidence that the targeted degree of security is actually achieved and remains effective; d) affords the customers the confidence that the agreed nature and degree of security is or will be attained. The requirements of a security printing management system are grouped in the following domains: Context of the organization, Leadership, Planning, Support, Operation, Performance evaluation and Improvement.
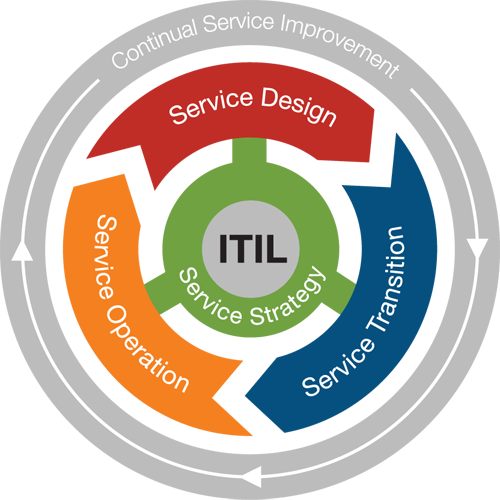
- IT Infrastructure Library (ITIL) - The global accepted best practice in service management, with large and small users in both private and
public sectors. IT Services Management focuses on Services, Quality, Organization and Policies. Service Support and Service Delivery are considered to be at the heart of the ITIL framework for IT Service Management addressing Service Level Management, Financial Management for IT Services, Capacity Management, IT Service Continuity Management and Availability Management. Service Support describes how customers and users can get access to the appropriate services to support their activities and the business, and how those services are supported covering: Service Desk, Incident Management., Problem Management, Configuration Management, Change Management and Release Management. ICT Infrastructure Management is concerned with the processes, organization and tools needed to provide a stable IT and communications infrastructure that is aligned with business needs at acceptable cost. Application Management provides an outline of the Application Management life cycle and is a guide for business users, developers and service managers of how applications can be managed from a service management perspective. Business Perspective is designed for business managers to understand IT service provision.
- Open Source Security Testing Methodology Manual (OSSTMM) - Provides a methodology for a thorough security test. An OSSTMM audit is an accurate measurement of security at an operational level that is void of assumptions and anecdotal evidence. CIA Information Assurance Objectives are mapped to Operation Controls as follows: Confidentiality: Confidentiality, Privacy, Authentication and Resilience. Integrity: Integrity, Non-repudiation, Subjugation and Availability: Continuity, Indemnification and Alarm. OSSTMM defines six types of tests, based on the amount of information the tester knows about the targets, what the
target knows about the tester or expects from the test, and the legitimacy of the test. Some tests will test the tester’s skill more than actually testing the security of a target. Blind - The Analyst engages the target with no prior knowledge of its defenses, assets, or channels. The target is prepared for the audit, knowing in advance all the details of the audit. A blind audit primarily tests the skills of the Analyst. Double Blind - The Analyst engages the target with no prior knowledge of its defenses, assets, or channels. The target is not notified in advance of the scope of the audit, the channels tested, or the test vectors. Gray Box - The Analyst engages the target with limited knowledge of its defenses and assets and full knowledge of channels. The target is prepared for the audit, knowing in advance all the details of the audit. Double Gray Box - The Analyst engages the target with limited knowledge of its defenses and assets and full knowledge of channels. The target is notified in advance of the scope and time frame of the audit but not the channels tested or the test vectors. Tandem - The Analyst and the target are prepared for the audit, both knowing in advance all the details of the audit. A tandem audit tests the protection and controls of the target. However, it cannot test the preparedness of the target to unknown variables
of agitation. Reversal / Red Team Exercise - The Analyst engages the target with full knowledge of its processes and operational security, but the target knows nothing of what, how, or when the Analyst will be testing.


